 CORPORATE IDENTITY
HISTORY
COCO CHANEL
PRODUCTS
CORPORATE IDENTITY
HISTORY
COCO CHANEL
PRODUCTS
The House of Chanel originated in 1909, when Gabrielle Chanel opened a millinery shop at 160 Boulevard Malesherbes, the ground floor of the Parisian flat of the socialite and textile businessman Étienne Balsan, of whom she was the mistress.[4] Because the Balsan flat also was a salon for the French hunting and sporting élite, Chanel had the opportunity to meet their demi-mondaine mistresses who, as such, were women of fashion, upon whom the rich men displayed their wealth as ornate clothes, jewellery, and hats.
Coco Chanel thus could sell to them the hats she designed and made; she thus earned a living independent of Balsan. In the course of those salons, Coco Chanel befriended Arthur "Boy" Capel, an English socialite and polo player friend of Étienne Balsan; per the upper class social custom, Chanel also became mistress to Boy Capel. In 1910, Boy Capel financed her first independent millinery shop, Chanel Modes, at 21 rue Cambon in Paris. Because that locale already housed a dress shop, the business-lease limited Chanel to selling only millinery products, not couture. Two years later 1913, the Deauville and Biarritz couture shops of Coco Chanel offered for sale prêt-à-porter sports clothes for women, the practical designs of which allowed the wearer to play sports.
Coco Chanel used jersey cloth because of its physical properties as a garment, such as its drape and how well it adapted to a simple garment-design. Sartorially, some of Chanel's designs derived from the military uniforms made prevalent by the War; and, by 1915, the designs and the clothes produced by the House of Chanel were known throughout France. In 1915, Chanel opened her very first Couture House in Biarritz, France. She had 300 employees and even designed her first line of Haute Couture.
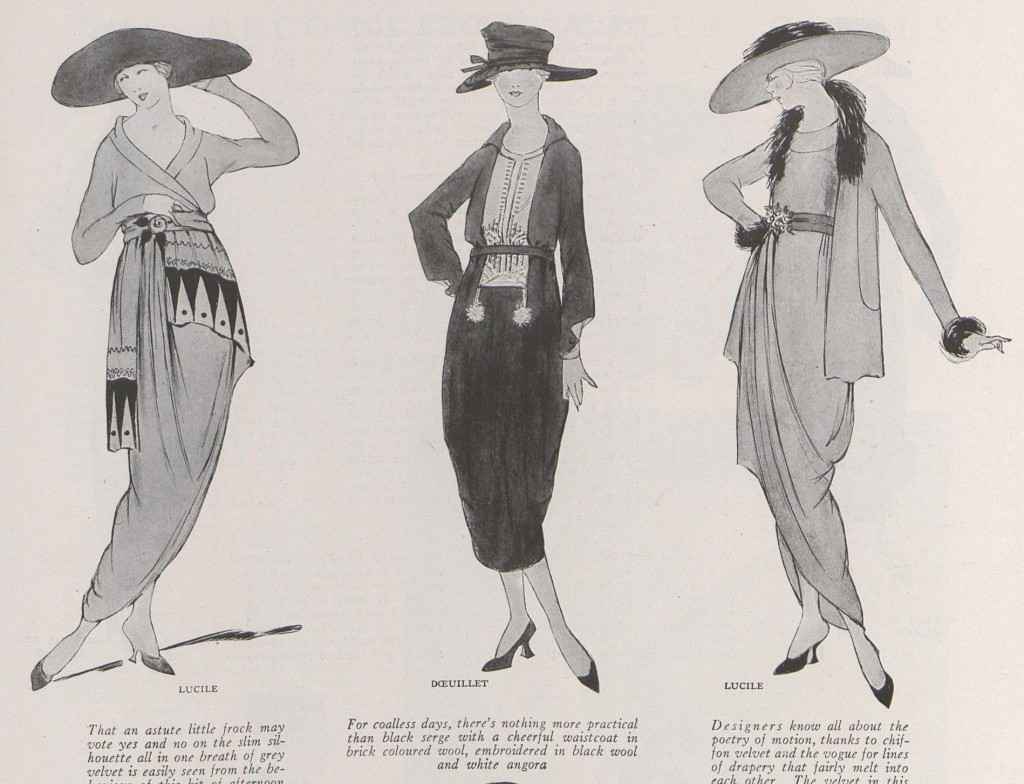
From the gamine fashions of the 1920s, Coco Chanel progressed to womanly fashions in the 1930s: evening-dress designs were characterised by an elongated feminine style, and summer dresses featured contrasts such as silver eyelets, and shoulder straps decorated with rhinestones, drawing from Renaissance-time fashion stylings. In 1932, Chanel presented an exhibition of jewellery dedicated to the diamond as a fashion accessory; it featured the Comet and Fountain necklaces of diamonds, which were of such original design, that Chanel S.A. re-presented them in 1993. Moreover, by 1937, the House of Chanel had expanded the range of its clothes to more women and presented prêt-à-porter clothes designed and cut for the petite woman. Among fashion designers, only the clothes created by Elsa Schiaparelli could compete with the clothes of Chanel.

During the Second World War (1939 to 1945), Coco Chanel closed shop at Maison Chanel, leaving only jewellery and parfumerie for sale, and moved to the Hôtel Ritz Paris, where she lived with her boyfriend, Hans Günther von Dincklage, a Nazi intelligence officer. Upon conquering France in June 1940, the Nazis established a Parisian occupation-headquarters in the Hôtel Meurice, on the rue de la Rivoli, opposite the Louvre Museum, and just around the corner from the fashionable Maison Chanel S.A., at 31 rue Cambon.
In 1953, upon returning to France from Switzerland, Coco Chanel found the fashion business enamoured of the "New Look" (1947), by Christian Dior; the signature shape featured a below-mid-calf-length, full-skirt, a narrow waist, and a large bust (stylistically absent since 1912). As a post-War fashion that used some 20 yards of fabric, the House of Dior couture renounced wartime rationing of fabric for clothes.
In 1947, after the six-year austerities of the Second World War, the New Look was welcomed by the fashion business of Western Europe because sales of the pretty clothes would revive business and the economy.
To regain the business primacy of the House of Chanel, in the fashion fields of haute couture, prêt-à-porter, costume jewellery, and parfumerie, would be expensive; so Chanel approached Pierre Wertheimer for business advice and capital. Having decided to do business with Coco Chanel, Wertheimer's negotiations to fund the resurgence of the House of Chanel, granted him commercial rights to all Chanel-brand products.
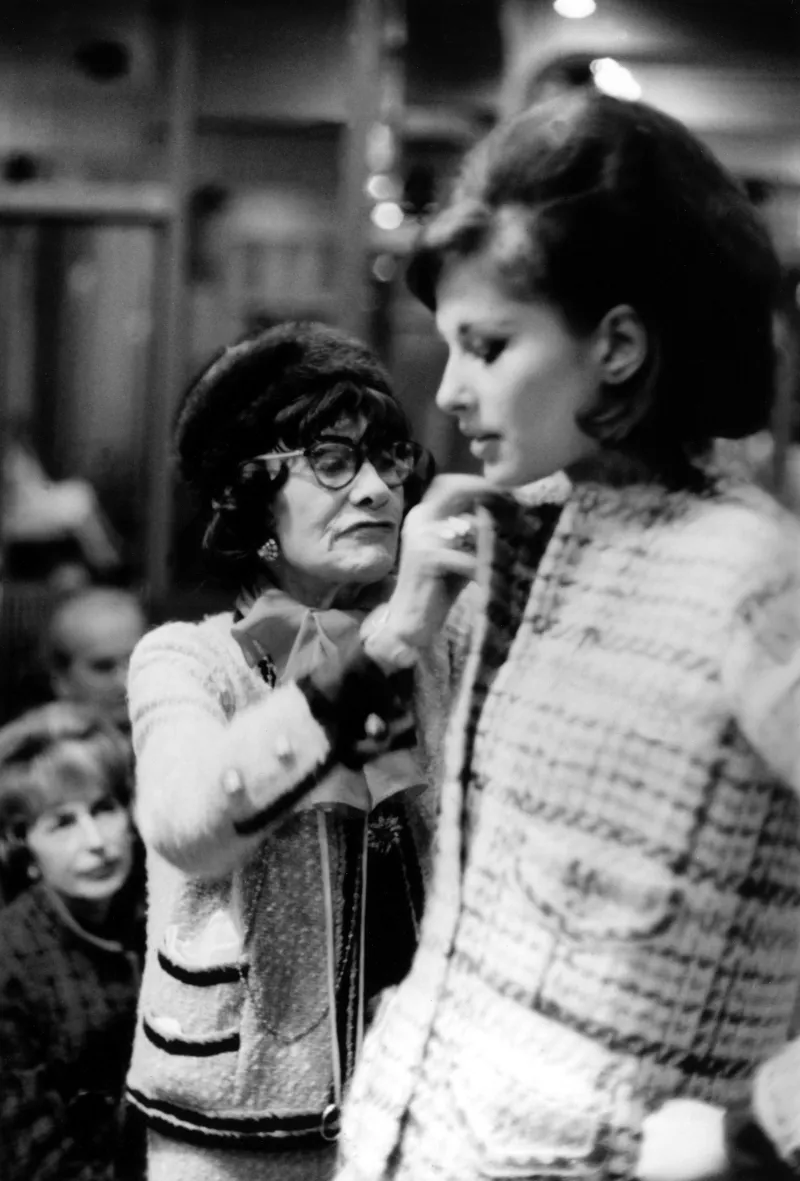

Coco Chanel died on 10 January 1971, at the age of 87.She was still designing at the time of her death. For example, in the (1966-1969) period, she designed the air hostess uniforms for Olympic Airways, the designer who followed her was Pierre Cardin. In that time, Olympic Airways was a luxury airline, owned by the transport magnate Aristotle Onassis. After her death, the leadership of the company was handed down to Yvonne Dudel, Jean Cazaubon and Philippe Guibourgé. So far, the bags designed by Chanel are still very popular in the vintage market.